The Science Behind High-Performance Braking
High-performance braking systems are critical components in modern vehicles, enabling rapid deceleration and maintaining control under demanding conditions. Far more than just simple friction, these systems integrate complex scientific principles, advanced materials, and sophisticated engineering to convert kinetic energy into heat efficiently and safely. Understanding the underlying physics and technological innovations involved reveals how these systems contribute significantly to vehicle safety and overall driving dynamics, from everyday transport to specialized racing applications.
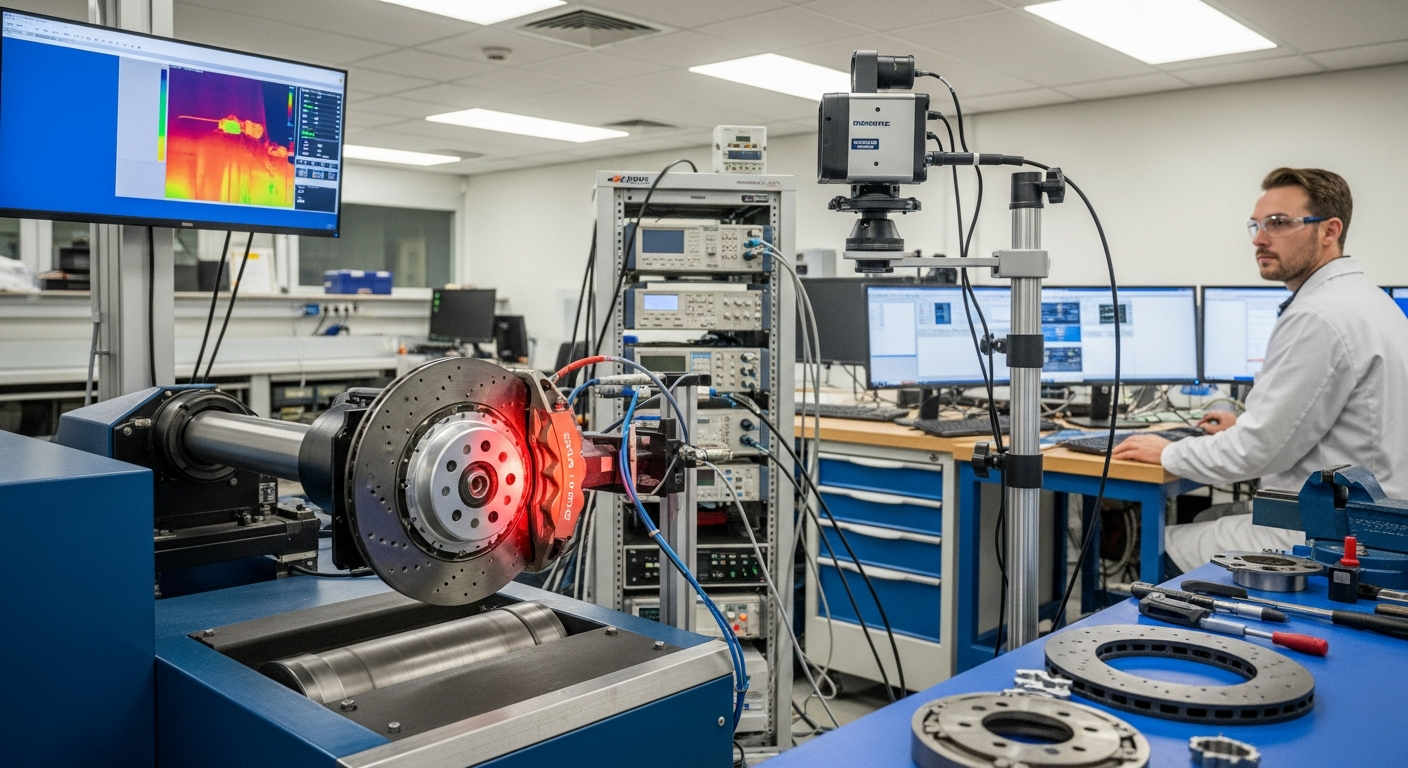
Understanding Braking Fundamentals for Performance
At its core, braking is the process of converting a vehicle’s kinetic energy into thermal energy through friction. In high-performance applications, this process must occur rapidly and repeatedly without significant loss of effectiveness, a phenomenon known as brake fade. The fundamental principle relies on the interaction between brake pads and rotors. When the driver applies the brakes, hydraulic pressure forces the pads against the rotating rotors, generating friction. This friction slows the wheels, and consequently, the vehicle. The efficiency of this energy conversion, and the system’s ability to dissipate the generated heat, are paramount for achieving superior braking performance and enhancing overall vehicle mobility.
Advanced Materials in Braking System Design
The materials chosen for brake components are central to a system’s performance and longevity. High-performance braking systems often utilize specialized materials for rotors and pads. Rotors can be made from high-carbon cast iron, which offers good thermal stability and resistance to warping, or advanced composites like carbon-ceramic. Carbon-ceramic rotors, common in luxury and sports vehicles, are significantly lighter and can withstand much higher temperatures, reducing unsprung weight and improving heat dissipation. Brake pads are typically made from a blend of metallic fibers, organic compounds, and ceramic particles, each formulation designed to offer specific friction characteristics, temperature resistance, and wear rates. The manufacturing processes for these components are precisely controlled to ensure consistent quality and reliability.
Engineering for Enhanced Safety and Control
Modern high-performance braking systems incorporate various technologies to enhance safety and driver control during deceleration. Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) prevent the wheels from locking up, allowing the driver to maintain steering control during hard braking. Electronic Brakeforce Distribution (EBD) automatically varies the amount of force applied to each wheel’s brake, depending on road conditions, vehicle speed, and load, optimizing stopping power and stability. Brake assist systems detect emergency braking situations and apply maximum braking force more quickly than a driver might manually. These innovations work together to provide predictable and stable stopping power, crucial for both everyday driving and extreme performance scenarios, contributing significantly to overall transport safety.
The Role of Aerodynamics in Braking Efficiency
While often associated with speed and stability, aerodynamics also plays a vital role in high-performance braking. Effective cooling of brake components is essential to prevent overheating and brake fade. Vehicle design incorporates specific aerodynamic features, such as brake cooling ducts, which channel airflow directly to the brake assemblies. This targeted airflow helps to dissipate the immense heat generated during heavy braking, maintaining optimal operating temperatures for the pads and rotors. Proper aerodynamic integration not only supports consistent braking performance but also contributes to the longevity of the components, ensuring sustained performance during intense driving.
Braking Systems in Modern Vehicle Technology
As vehicle technology continues to evolve, so do braking systems. Electric and autonomous vehicles introduce new considerations and opportunities for innovation. Electric vehicles, for instance, extensively use regenerative braking, where the electric motor acts as a generator during deceleration, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy to recharge the battery. This not only improves fuel efficiency but also reduces wear on the conventional friction brakes. For autonomous vehicles, braking systems must be seamlessly integrated with sophisticated sensor arrays and control algorithms, ensuring precise and reliable stopping without human intervention. The integration of advanced sensors allows for predictive braking, anticipating obstacles and optimizing deceleration for passenger comfort and safety.
Fuel Efficiency and Sustainability in Braking
While braking inherently consumes energy, advancements in high-performance systems can indirectly contribute to fuel efficiency and sustainability. Lighter brake components, such as carbon-ceramic rotors, reduce overall vehicle weight, which in turn lowers the energy required for acceleration and improves fuel economy. Regenerative braking in electric vehicles directly conserves energy, extending range and reducing the overall energy footprint. Furthermore, the development of more durable materials and designs leads to longer-lasting components, reducing the frequency of replacements and minimizing waste. This focus on material science and energy recovery aligns with broader goals of environmental sustainability in the automotive industry, impacting how vehicles consume fuel and manage their engines’ energy output.
High-performance braking systems represent a pinnacle of automotive engineering, combining fundamental physics with cutting-edge material science and sophisticated electronic controls. These systems are essential for the safety, control, and dynamic capabilities of modern vehicles, from ensuring reliable daily transport to enabling the extreme demands of competitive driving. Continuous innovation in design, materials, and integrated technology ensures that braking systems will continue to evolve, meeting the increasing demands for safety and performance in the future of mobility.






